Ranking high in search engine results pages (SERPs) for specific keywords and getting more exposure requires you to optimize multiple factors that search engine use in its algorithm. This includes on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO.
In this post, we will discuss what on-page SEO is and on-page SEO factors.
Let’s get started…
What Is On-Page SEO?
Also called on-site SEO, on-page SEO involves optimizing your web pages to improve website ranking on SERPs. To be more specific, on-page SEO involves optimizing the internal aspects of your website to make them both search engine friendly and user-friendly.
By internal aspects, we mean website elements such as HTML tags and website content, including text, image, audio, and video content. You need to ensure these things are optimized as per the latest search engine best practices.
If you focus on on-page SEO, search engines will understand the content on your website better and also easily assess the relevance of your content in relation to the queries asked by your target audience. This means better ranking and more traffic.
To reap the optimal benefits of your on-page SEO efforts, you need to address all the components of web pages.
9 On-Page SEO Factors for Better Search Engine Ranking
Paying attention to these crucial areas will help boost ranking and traffic to your site.
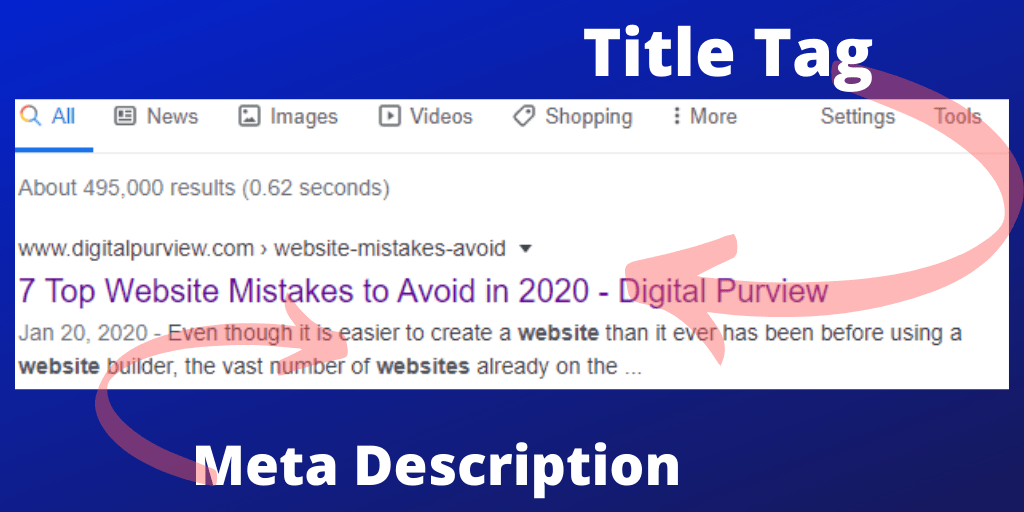
1. Title Tags
A page should comprise different meta tags, starting with the title tag. The title is what your visitor sees on the search engine, followed by the meta description, which we will discuss later on.
Your title tag should give the reader a clue of what to expect in the content of the page. Make sure it is relevant to your content as Google compares the title tag and the rest of the content when ranking web pages.
Also, ensure that it contains your page’s main keyword and doesn’t exceed 65 characters. Although it doesn’t have a lot of impact on your ranking, make sure your title tag is unique and interesting to increase the click-through rate (CTR).
2. Meta Description
After the title tag, there are a few words that appear on search engines before you click through to a page. These sentences under the title are known as Meta description.
Your Meta description should describe your page content in a more in-depth way than your title. Make sure it is unique to give you a competitive advantage and increase your CTR. If it’s possible, integrate your page’s main keyword into your Meta description.
3. Heading Tags
Your web pages should be divided into subtopics with subheadings (heading tags). Heading tags start with H1 to H6, with the most important being the H1 tag. Having several heading tags aid in navigation.
4. Schema Markup
Also called structured markup, schema markup aids search engine bots to understand the content on your web page. If you have observed search engine results lately, you will have noticed most come with reviews, star ratings, or images. These are schema markups, and they aid in increasing CTR.
Our eyes are attracted to visuals, which is why it is important to have visuals on your pages, especially if you are selling something. Although having schema markup on your pages has minimal effect on your ranking, it increases CTR in SERPs.
5. Image Alt-Text
While images help to make your content interesting, they can also form an important part of your on-page SEO when optimized.
Since search engine bots cannot understand your image content, you should use alt-text. Image alt-text describes what your image is all about. This is what search engines use to crawl your images.
You can include a keyword in your alt-text to boost your ranking. Make sure only to use them when it is applicable to avoid getting penalized for keyword stuffing your content.
6. Page URLs
A uniform resource locator, popularly known as a URL, is the specific address to a web page. URL should tell what your page is all about, and thus should be relevant to your page content.
To optimize your web page URLs, make sure they have your page’s main keyword. Also, ensure they are readable and relate to your domain name. Avoid keyword-stuffing it and using special characters. Keep it simple.
7. Inter-linking Pages
One of the highly impactful aspects of on-page SEO is internal linking. You should link your pages to help both the search engine and users navigate your site with ease.
Also, add a text link or even an image link to your page content by using anchor tags. By interlinking, you not only help search engine bots crawl your site, but also aid navigation on the part of your visitor.
In other words, internal linking makes your website user-friendly and understandable to search engines. This helps to boost your website’s overall ranking.
8. Web Content
Web content is a wider aspect, and that’s why I have opted to describe it as the last on-page SEO element. All the above on-page SEO factors will be of minimal impact if you don’t create quality, relevant content to rank. Visitors come to your website to read your content unless you have an eCommerce site.
That’s why it is mandatory that you create quality, relevant content if you want your on-page SEO efforts to pay off. All the above elements should come after you have created great content that is helpful to your target audience.
Quality, Relevant Content
By quality, relevant content, We mean
i. Original content
Your content should be unique and not generalized. It should include videos, infographics, or any other visual to supplement it.
ii. Meeting the searcher’s keyword intent
You should create content around your searchers’ keywords. In other words, provide a solution to your searcher’s problem.
iii. Non-text content
In addition to your text content (articles), you should have other types of content on your website, such as videos and image content.
No Low-Quality Pages
Keep in mind that since the launch of the Google Panda algorithm in 2011, Google has been more geared towards promoting content-focused pages while devaluing low-quality pages. The main purpose of the Google Panda algorithm is to reward websites with relevant, high-quality content by ranking them higher in SERPs while demoting those with low-quality content.
Here is what Google terms low-quality content.
i. Thin content
Web pages with highly-summarized content or even no content at all are said to have thin content. Improvement in technology has enabled Google bots to detect pages with thin content that is not helpful to a reader. For instance, a health page describing a serious health condition in 4 or 5 sentences will not be helpful. Normally, someone who is looking for information about a serious health condition naturally expects it to have detailed information on causes, symptoms, mode of treatment, etc. Naturally, you cannot describe all these in 4 sentences.
ii. Duplicate content
Google takes plagiarizing or duplicates content issues seriously, which is why you should create unique content for your web pages.
iii. Misleading content
There are web pages that use irrelevant keywords for the sake of ranking and getting more traffic. If your keyword fails to match your content, Google bots will still catch up with you, and you will be penalized.
iv. High ad-to-content ratio
Web pages with heavily paid ads display that overwhelm their content interfere impact user’s experience negatively. Such websites risk being devalued
Other issues that devalue your content include keyword stuffing, low-quality affiliate links, spun content, many grammatical errors, etc.
Remember to integrate relevant keywords in your web pages and strategically place them in the right places, such as in your content title, subheadings, and first paragraph.
That’s why you should create quality content that offers value to your readers. Once you have created quality content, you can start focusing on the other elements of on-page SEO.
9. Outbound Linking
Also called external links, outbound links are links that send your site’s visitors to other websites across the web. They are commonly used to back up sources, verify facts, or point people to better resources.
These links work in the opposite way as inbound links, whereby other websites send their visitors to your site, but we will discuss this in another topic.
Outbound links can be of two types- nofollow and dofollow. The no-follow simply has Rel=”nofollow” in their link HTML.
In short, nofollow tells search engines not to crawl the links (not to follow the links) while dofollow links can be crawled and thus pass on your ranking power to the site you are linking to.
How do outbound links boost your SEO and why should you use them?
Well, there are three benefits of using outbound links;
i. Help increase relevance
Search engines can learn what your site is about from the site you are linking to. You can think of these links as clues to crawlers about the niche you are in and what you are trying to address. This can help you rank higher since Google understands your content better and thus can better match it to a specific searcher’s query.
ii. Better Reputation
When you are linking your website to a high-authority source, you can boost your reputation. This works in the form of association.
iii. Encourage backlinks
Outbound links can lay a foundation for future relationships with other bloggers, websites, and journalists. Endorsing their work can encourage them to return the favour as well. This will be beneficial to your ranking since you will get a backlink from an authority site.
As you can see, outbound links can be beneficial for your ranking purposes. Just to remind you, when using outbound links, always look for natural linking opportunities, ensure your links open in new tabs, and avoid overdoing them.
Bottom Line
These are the main elements of on-page SEO, and we do hope that you now have an idea of where to start. On-page SEO helps to make it easier for Google to crawl and understand the content on your site and also makes your website user-friendly.


