- What is text to HTML ratio?
- Does it contribute to SEO?
- Which changes can make a difference?
Text to HTML ratio is a debatable topic in SEO. Some SEO tools include it as a key parameter of SEO health, while many SEO experts completely ignore it.
Let’s learn all about the text-to-HTML ratio to enable you to use it for the benefit of your website.
What Is Text to HTML Ratio?
In simple words, you can say that the page of a website is written in HTML code, and the website’s content is displayed in text. The text-to-HTML ratio is the percentage of content available on that particular webpage.
You can manually check it by going through the text displayed on that page to know the text-to-HTML ratio. You can also use an online ratio checker for this purpose.
Does Text-to-Code Ratio Matter for SEO?
The ratio does not matter much when it comes to SEO. Google has even confirmed that they don’t use this ratio as a ranking signal.
But when the ratio is lower, it might create confusion for search engines. This ratio in itself does not help much to boost the visibility of your website. The search engines will evaluate your website depending on the quality and genuine content. They will not use quantity to boost the ranking.
However, a poor text-to-HTML ratio can often signal other SEO issues, so you can still use it especially if you are just starting out with SEO. Let’s understand the use in more detail.
Thin Content Issues
The lower ratio means less text. When the text is less, the crawlers will not have sufficient information about your website. If the machines are not able to know the objective of a website, they will not know for which search queries your website should be presented in search results.
The result is obvious. Your website will not appear on the first page of search results and may not appear at all. Also, when the information is less, your potential customers might not find your website worth visiting.
Therefore, you need to make a good balance of quality content and code to boost the visibility of the website and win the trust of visitors as well.
Inefficient Code Issues
Another point to keep in mind is the code limit. You should use the minimum possible code required. If you realize that the text-to-HTML ratio is low for your page even if you have enough content, then it might be an indication of unnecessary coding.
When you have many codes, it might affect the speed of loading the webpage. The loading speed decides Google’s ranking as well. Therefore, it is essential to make a proper balance to avoid such a possibility.
You will have to choose the right amount of code as well as the text. The text needs to be relevant and genuine as well. After all, the objective of your website is to reach a larger level of the target audience. That objective is only possible with high rankings in search engines for relevant keywords.
How to Calculate Text to HTML Code Ratio
You can manually check the ratio or use one of the many online tools to do this for you. Let’s go thru both these methods.
Manual Method
To calculate the ratio manually, you need to find out the size of your HTML code and the size of your text content. Here is the step-by-step process and formula.
- Take the source code of your webpage and save it in notepad. There are many ways to get the source code (e.g. right-click on a webpage in Chrome browser and click view page source). Note down the size of this notepad. This is the size of your webpage with both code and content.
- Remove all the code from the notepad leaving only text content. Note down the size of this notepad. This is the size of your text content.
- Subtract the size of the text content notepad from the size of the webpage notepad. This is the size of your code.
- Calculate the ratio as
(Size of text)X100/(Size of code)
As you can see this process is quite cumbersome. Let’s look at the easier method.
Online Text to Code Ratio Checking Tools
There are many free online tools such as this calculator that can do this calculation for you. You just need to enter the URL of your webpage and the tool will calculate the ratio.
However, as mentioned earlier this ratio in itself does not matter for SEO but can point to other SEO issues such as thin content or inefficient code. So, it is always a good idea to combine this ratio with a technical site audit and an on-page site audit to improve overall SEO health.
Many SEO tools such as SEMrush include this ratio in the site audit and calculate the ratio automatically for you for all of your web pages. You can then look at this ratio along with other SEO parameters such as low word count and inefficient code.
What Is a Good Text-to-HTML Ratio for SEO?
So, what is a good text-to-HTML ratio to target? Some experts believe a good ratio is 25 to 70. SEMrush calls out an issue when the ratio is below 10.
I did research on the 1st-page result of a few competitive search queries to check the text-to-code ratio and this is what I found.
- Average ratio: 17.4
- Median ratio: 17
- % Results with a ratio above 25: 20%
- % Results with a ratio below 10: 20%
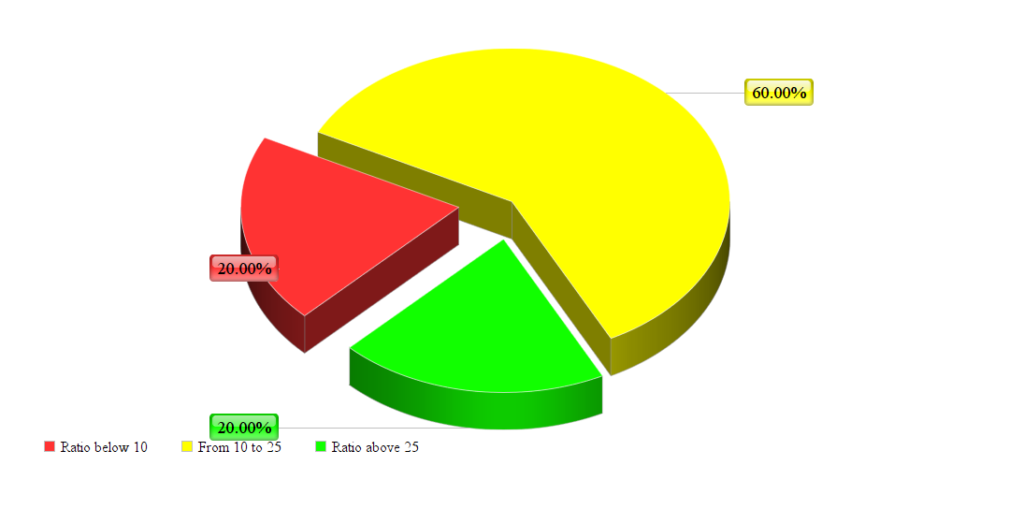

As you can see, most of the results were well below 25 and 20% of results were even below 10.
If we combine this learning with Google’s statement earlier, I don’t think there is any ratio that is particularly good or bad. You should just see this ratio as an opportunity to improve your webpage.
For example, if some of your pages have this ratio much lower than others, then investigate further if this is an issue. It is perfectly fine for some of the pages (e.g. contact page) to be low on content and ratio.
How to Improve Text-to-Code Ratio
Now you should have an idea about the text to HTML Code ratio. You know what exactly it is and how to make a proper balance to get the optimum ratio. If you still have some doubts, consider going through the following.
As you know, the ratio is all about the balance between HTML code and the content of a webpage. You should use the right amount of content. At the same time, you should consider removing unnecessary code, plugins, and add-ons. These unnecessary things can confuse search engines.
Let’s cover some more details.
- The HTML code of a website needs to be appropriate and valid. If you have any doubts about the code of a specific page, take the time to use online tools such as this HTML checker. If you are using WordPress or website builders such as Wix, make sure to add only reliable and required plugins and third-party codes.
- Be mindful of the code limit. You should use the minimum required code. If you realize that the text-to-HTML ratio is low for your page even if you have enough content, then it might be an indication of unnecessary coding. In that condition, you can review and minimize the code to make the ratio appropriate.
- You should make the size of your web page as small as possible. Avoid plugins with heavy code. If you are using WordPress, use a lightweight theme. You should also avoid too many plugins and add-ons. Also, too many comments, large white space, JavaScript, and similar things can increase the code, and that is going to affect the ratio.
You can consider all the things mentioned above to get the optimum ratio. Make the design simple but effective. If you add many elements, it might impress your visitors. But it might affect the visibility of your website in search engines.
Wrapping Up
Even if the text-to-HTML code ratio does not matter much to boost SEO, you should try your best to keep the code simple and clean to get high rankings in search engines. This step also helps to maintain a good ratio and get an enhanced user experience.
The text-to-HTML ratio of a website is also an indicator of the text size. However, always remember that more text will not help with a higher ranking. The key is to have quality and genuine content. Neither the search engine nor your target audience is going to appreciate more content when it does not serve any purpose.


